Welding is the cosmic union of metals, a fiery embrace that transforms separate pieces into a singular, unbreakable bond. It involves joining two or more pieces of metal simply by melting them through applying heat and in turn fusing them together.
This heat is generated by an electric arc, gas flame, or laser. After melting the materials when they solidifies, a strong and durable bond of metal emerges. The final form of solidified metal is called the weldment.
Welding is the alchemy of creation, the fusion of form and function that shapes the backbone of our world.
So, whether it’s skyscrapers touching the sky or the humblest of joints holding things together, welding is the celestial glue that binds the tangible dreams of humanity.

How Does Welding Work?
The welding process is all about heat and melt the metal. It begins with the selection of the right welding method – be it arc welding, MIG, TIG, flux, oxy-fuel, solid state or another.
Then, enter the welder machine, armed with power source, electrodes, torches, filler material and ground clamps. With all the equipment’s in hand now it time to to conduct the metal orchestra.
Firstly, the metal surfaces to be joined are meticulously prepared, cleaned, and aligned of dust, rust and contamination. Then welder machine needs to set up for job.
When the main switch is turned on, the power source from the welder machine flows the electric current to electrode and ground clamp.
Note: All welder machine has two terminals one is positive and another negative. As a welder you need to connect the cord of electrode or torch to one receptacle (either positive or negative) and a clamp is needed to connect to the other terminal. Where you should connect the cords depends on polarity settings. Read this article on DCEN & DCEP polarity for more information.
The connection completes the circuit & creates an arc. As a result it cues the heat – intense and focused on the workpiece and base metal. Whether it’s an electric arc, a stream of molten metal, or a laser beam, the goal is to bring the materials to their melting point.
As the base metals become the molten pool, the welder introduces the filler material, a metal rod with flux or without flux, that participates into melting & fusion process.
Now it’s all about controlling the travel speed, the angle & the pressure to create a seamless connection. The better you can control the gun and arc flow rate, the better the quality of weld becomes.
Finally, after melting and fusing as the heat recedes, the once-fluid metal solidifies into a strong bond. The result is a strong joint, a fusion of two parent metals into one, where strength and resilience reign supreme.
Some welding technique like solid state welding works differently. Here you don’t need electric arc to fuse the metals. Only the pressure & heat is enough in this case.
Plastic welding works same as spot weld or solid state welding. Here comparatively lower temperature and pressure are applied to melt and join plastic materials. With the help of modern technology, now wood welding is also possible.
In wood welding linear friction process is used. Here pressure and friction is applied on special types of wood to make them one. Here heat and pressure are centered between two wood pieces which in turn makes the wood fibers to join together.
What You Need To Weld
You must have the following equipment’s and accessories to start welding. The requirements may vary depending on the projects and type of welding. We have focused on arc welding here and given the tools you need for arc welding. For other types of welding you don’t need that much elements that’s why we have mentioned them at the end.
- Welding Machine : This welding machine itself is the heart of welding. It converts electrical energy into heat that is essential for melting the metals. Welder can be multi purpose welder and single purpose like dedicated mig, tig, stick, flux or plasma welder. Choose one wisely based on your welding style, project and needs.
- Welding Helmet: Helmet is must while arc welding. when you weld, metal particles, bright light, gasses, harmful fumes and arc sparks comes out of weld pool. If not shielded well, they can cause harm to your eyes, respiratory system and face. So to guard against all the harms of welding you need a quality welding helmet. You may also use additional face respirator for more protection.
- Leather Gloves: Meet your hands’ best friends – flame-resistant, durable gloves that provide the ultimate protection. It saves your hand from getting burnt from the high temperature of welding, protects hands from metal particles being pierced into hand. Also it helps you to save your hand from getting cut from metal pieces.
- Welding Electrodes: Depending on welding technique you would require to have various electrodes. For stick welding you need electrode rod with flux around it, for mig welding you need mig solid wire spool, for tig welding you need tungsten electrode and for flux core welding you need flux cored mig wire or wire with flux around it.
- Welding Filler Metal: You are going to need filler metal for almost all types of welding except stick welding. In stick welding electrode is enough but for tig welding, mig welding and flux core welding you must have a filler metal. Filler metal can be of stainless steel, mild steel, silver even gold. In welding, brazing and soldering filler metal is heated to melt and flow into the join of the parent metal and workpiece. They have generally lower melting point from base metal.
- Welding Clamp: Every type of welding require a ground clamp connected to the either positive or negative terminal of the welder machine. The clamp is placed on the base metal and electric circuit is completed to enable the flow of electricity to the electrode holder or torch.
- Torch Or Electrode Holder: In mig, tig and flux core welding, you are going to need a torch or a welding gun. It evolves the electrode wire to feed into the weld pool creating an arc at the tip of the gun or torch. For stick welding, you need an electrode holder that holds the stick rod and creates an arc with the electricity flowing through it.
- Steel caped toe boots: Boots are important to wear while welding. This helps to protect your feet from being burnt and electrocuted while you come to the contact of welding electric wire.
- Leather Jacket: Jacket is required to ensure safety from welding arc. It protects your body from getting electrocuted also.
- Chipping Hammer and Wire Brush : After welding you need to Cleanup the dirt’s. A chipping hammer removes slag and impurities, while the wire brush gives your weld a polished, refined look.
- Welding Table: The welding table provides a sturdy, level surface for your metal pieces and hold them together. It’s where your ideas take shape and where sparks of creativity fly.
- Other Accessories: There are many other accessories you need to start welding. For example anti spatter spray, weld primer, paints, sander, grinder machine and so on. They support the welding job for better result.
What Types Of Metal Can You Weld
Welding is a versatile art, and you can weld a variety of metals, each with its own characteristics. Most basic types of metals that are welded widely are given bellow-
- Steel : Whether it’s mild steel, carbon steel, stainless steel, or high-strength alloy steel, you can easily weld them. They are robust, malleable, and widely used in various applications.
- Aluminum: With light-weightness and corrosion-resistance qualities, aluminum is a favorite in aerospace and automotive industries. Welding aluminum demands finesse due to its lower melting point. Tig welding is the best choice for seamless aluminum welding. You may also use mig for the purpose. Only require a spool gun for bet finish in this case.
- Stainless Steel: Resistance to rust and corrosion, stainless steel is the go-to for applications where hygiene and durability are paramount. It requires specific techniques like shielding gases to prevent contamination while welding stainless steel.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron requires a skilled hand for precise welding. Its high carbon content makes it prone to cracking, but with the right approach, you can mend and restore vintage cast iron pieces.
- Copper: Known for its excellent electrical conductivity, copper is prevalent in electrical components. Welding copper demands precision to avoid overheating and oxidation.
- Nickel Alloys: Commonly used in high-temperature environments, nickel alloys exhibit exceptional heat resistance and corrosion properties. Welding these alloys requires expertise to maintain their unique characteristics. You can also weld chromoly like nickel alloy.
- Titanium: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, titanium is a staple in aerospace applications. Welding titanium demands meticulous control due to its sensitivity to contaminants.
- Brass and Bronze: Beyond their aesthetic appeal, brass and bronze find their way into artistic and decorative welding projects. Welding these alloys requires attention to prevent overheating and maintain their color. Oxy fuel and solid state welding process are the best choice for brass & bronze.
- Gold: It may sound surprising but gold can also be welded. You can use soldering or oxy fuel welding techniques for better result.
Remember, each metal comes with its own set of challenges and nuances. Understanding the properties of the metal you’re working with is key to unlocking the full potential of your welding prowess.
Basic Types Of Welding
There are various types of welding process available today in welding industry. They are
1. Arc welding
Arc welding is a widely employed welding process that utilizes an electric arc to join metals. It involves automatic, semi-automatic and manual process. Most common Arc welding techniques are
i) Mig welding (GMAW) or metal inert gas welding
ii) Stick welding (SMAW) or Shielded metal arc welding
iii) Tig welding (GTAW) or gas tungsten arc welding
iv) Submerged Arc welding (SAW) and
v) Flux core arc welding (FCAW).
Note: Find the dedicated article on arc welding for deep understanding on Arc welding Process basics.
2. Electron Beam Welding
Electron Beam Welding (EBW) is an advanced welding process that utilizes a highly focused, high velocity electron beam to join metals with precision. In EBW, electrons are accelerated to high speeds and concentrated into a narrow beam, directed at the welding point between two materials.
The kinetic energy of the electrons generates intense heat upon impact with the work pieces, causing them to melt and form a metallurgical bond as they cool.
The whole process is performed in a vacuum chamber so that no beam electron is scattered. This technique is very controlled and efficient. The process is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries where intricate and high-strength welds are crucial.
3. Friction Welding
Friction welding is a solid-state welding process that joins materials through the application of mechanical friction. This can be done in different way on materials like steel, aluminum even on wood.
In this technique, two work pieces of materials are brought into contact and subjected to rotational or axial motion under pressure. The motion creates heat and eventually fuse the materials together without reaching a molten state.
There are various types of friction welding, including rotary friction welding (RFW), linear friction welding (LFW), and friction stir welding (FSW). Each of them offers a unique advantages for specific applications.
Note: Learn the basic of Friction Welding Technique in a dedicated article for better understanding.
4. Laser Welding
Laser welding use concentrated head to melt and fuse on specific point of metals and plastic. This process ensures deep penetration of weld with high accuracy and joining rate. This process requires less effort to weld metals and mostly used in automotive industry.
Laser welding is performed with high frequency modern laser welder that can easily concentrate its laser beam onto a specific point and join the metals in a speedy way. It doesn’t require a vacuum chamber like electron beam welding.
5. Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a type of welding where no electric arc or laser beam is required to melt and fuse the metals. Instead, it uses heat and pressure to clamp two metals together. There are mainly two types of resistance welding. One is Spot welding and another one is resistance seam weld.
- In spot welding, two or more metal sheets are joined by the application of heat and pressure at localized points. In the process, heat is applied through electrodes and electrodes direct an electric current to the metal sheets, creating resistance and generating heat. The heated metal softens, and pressure from the electrodes forms a weld nugget, resulting in a quick and efficient bond.
- In seam welding rotating wheel electrodes apply pressure to the materials while an electric current passes through, creating localized heat. The continuous movement of the electrodes along the seam results in a continuous, leak-tight weld.
Common Types Of Welding Joints
There are basic 5 kinds of joints in welding. There are as follows-
1. Butt joint

A butt joint in welding is a common connection where two pieces of material are joined along their edges in a flush manner. Welding a butt joint involves melting and fusing the edges together which creates a strong and integral weld. In Butt joint, metals are fused at an angle of 135-180° inclusively in the joint point.
2. Tee joint

In welding, a tee joint is formed when two materials are connected at a right angle (90° angle), resembling the letter “T.” Welding a tee joint involves fusing the end of one material to the middle surface of another, creating a joint that is commonly used in the construction of frames, brackets, and various structural components.
3. Corner joint

It is corner to corner joint. That means in this joint one pieces of metal is welded to another pieces side by side in between 30° to 135° angle making an “L” shape. Normally tubular pipes and sheet metals are jointed in this way.
4. Edge Joint

An edge joint in welding refers to the connection of two metal pieces along their edges, creating a seam that is welded to join them together. In this type of joint, two pieces of metals are connected in 0-30° angle.
5. Lap Joint

Lap joint is an overlapping joint. It involves welding two metal pieces overlapping each other, at 0-5° angle creating a strong and bold connection. This types of joints is used for applications ranging from sheet metal assemblies to more complex structures.
5. Cruciform Joint

A cruciform joint in welding is formed when two pieces of metal intersect at right angles, resembling the shape of a cross.
Other Welding Joints
- Slot Weld
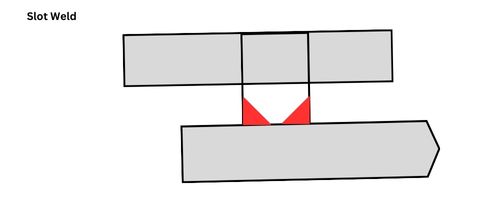
A slot weld in welding involves joining two overlapping metal components by filling a slot or groove with filler metal. This type of weld is commonly utilized in applications where a flush and aesthetically pleasing joint is desired.
- Plug Weld

A plug weld in welding is formed by filling a hole or opening in one metal piece with molten weld metal, creating a secure bond between the two connected components.
- Full Penetration

A full penetration weld in welding refers to a joint where the weld metal extends completely through the thickness of the materials being joined, ensuring a strong and continuous bond.
- Partial Penetration

A partial penetration weld in welding involves joining two materials with weld metal that partially penetrate through the entire thickness of the joint.
- Single Side Weld

A single-side weld in welding involves the application of weld metal on only one side of the joint, leaving the opposite side unaffected.
- Double Side Weld

A double-side weld in welding involves applying weld metal on both sides of the joint, ensuring complete penetration and bonding between the materials.
Welding Position
Welding positions are standardized orientations used to describe the relative placement of the welding joint and the welder during the welding process.
The American Welding Society (AWS) has established a set of welding position codes to provide a common language for specifying welding requirements. There are four primary welding positions.
They are-
- Flat Position (1F/1G): The welding is performed on the upper side of the joint in flat position. It is done on the horizontal face.
- Horizontal Position (2F/2G): The welding is done along the axis of the joint, in horizontal position. For groove welds the joint is in the vertical plane.
- Vertical Position (3F/3G): The welding is performed from the bottom to the top of the joint in vertical potion
- Overhead Position (4F/4G): In the overhead position, the weld face is at overhead. And the welding is done on the lower side of the joint.
How to learn welding
Welding is a technical work that’s why many people think it is difficult. But if you follow the welding rules, learning to weld is not that complex. You may need to practice for a long time to become master on welding.
You may follow the steps mentioned bellow to learn welding.
- Enrolling in welding school or vocational training institute
- The best way to become a certified welder is to get addition to a welding school. You may consider taking a welding class at a local trade school, community college, or vocational training center. In-person classes often provide hands-on experience under the guidance of experienced instructors. With the instructors supervision you would learn welding earlier. And of course you must practice a lot to become a good welder.
- Working as an apprentice in garage or workshop
- That is another way of learning to weld practically. You just need to contact a garage or workshop and become an apprentice to learn welding hand on experience. You may need to pay them for your intern or you may work for a slight remuneration. You will have a great chance to master the welding in this way as you will have real life experience with various types of works.
- Networking and Job Opportunities
- Attend industry events, join online communities, and network with professionals in the field. This can lead to valuable connections, job opportunities, and exposure to different aspects of welding.
- Reading blogs and practice
- You need to know the basic welding terms and definitions. Blogs and article on the web can help you in this regard. You should follow blogs from experts where they impart their experience, provide notes and tips to follow while welding and technical know-hows. You can follow their tips and apply on welding at home.
Note: Start with easy welding process like Mig welding and try to work on simple project first. Don’t go for large and complex projects at the beginning of your welding journey.
- Watching video
Videos are an important medium of learning this days. You can watch videos on welding and learn from them obviously you need to practice the technique as soon as you finish watching the video. Follow every steps and do it yourself at home.
Note: Make sure you are safe while welding. Wear necessary safety equipment’s and arrange a clean, dust free and well ventilated place to practice welding.
- Buying online course
The main problem with blogs and videos are, they are not chronological and following any syllabus. You need to learn welding step by step, one technique after another. But in most of the case you won’t find a free resource that follows the order.
So the solution is to buy a welding course. There you will find step by step welding following a syllabus that will ease the learning journey and make your welding journey smooth.
Note: I have listed some best welding courses online you can buy to learn from experts. Check that out for more details.
Moreover, there is no alternative to practice by yourself. Even if you are getting tuition from the best welder in the world, but not practicing at home you will learn nothing. Welding is a technical job so you must follow the rules and practice regularly either at home or at workshop.
Steps of welding
- Prepare material: You need to prepare metal before weld. Clean the metal if there are darts or rust on the metal. Grind them off if necessary.
- Choose welder: Choosing a good quality and suitable welder is a basic thing. You need to choose one according to your need. For example for mig welding you need a mig a welder and for tig welding you need a tig welder. And if you want to save money try buying a multi-process welder.
- Ready the accessories and configure them correctly: You need to configure the welder before starting the weld. Try the default settings first and connect the plug well with the receptacles. Plug the torch and work piece clamp correctly. Check the gas flow in case of mig and tig welding.
- Start the welder: After that start the welder by switching the on button. Check everything is ok and start with a single pass first to check the weld quality.
- start with fit and tack: First follow the back and forth technique. Make a tack first on two edges of the metal and then start filling the filler continuously to finish the welding.
- First slow pass then full pass with required speed: Don’t start with fast welding. First make a tack and slowly move the torch forth with a lower travel speed. Gradually increase the speed to ensure perfect pass.
Important terms in welding
- Parent metal
In welding, the term “parent metal” refers to the base material or the metal that is being joined together.
- Filler metal
Filler is a metal that is added during the welding process to join two or more pieces of base or parent metal.
- Weld metal
Weld metal refers to the portion of a welded joint that has been melted and subsequently solidified during the welding process.
- HAZ (Heat Affected Zone)
HAZ stands for “Heat-Affected Zone” in the context of welding. The Heat-Affected Zone is an area of a material that has experienced changes in its microstructure and mechanical properties due to the heat generated during welding, cutting, or other thermal operations.
- Fusion zone
The fusion zone is a specific region in a welded joint where the base metals have been melted and fused together during the welding process.
- Weld zone
The term “weld zone” is often used as a general reference to the entire area affected by the welding process. It encompasses various regions, each with its own characteristics.
- Weld face
The term “weld face” generally refers to the surface of the welded joint where the materials have been fused together.
- Weld toe
The term “weld toe” refers to the junction between the weld face and the base metal in a welded joint.
- Weld root
The “weld root” refers to the point or line where the back or root side of a weld joint is formed.
- Excess Metal: “Excess weld metal” refers to the amount of weld metal that extends beyond the specified dimensions or requirements for a particular welding joint.
- Layer
In welding, a “layer” refers to a single pass or deposition of weld metal applied during the welding process. Welding often involves building up a joint by depositing multiple layers of molten material, typically using a filler metal.
How much a welder do makes?
Welding is a lucrative job in case of money. Statistics of USA BLS shows that, welders can earn on average $35000-$500000 per year at the starting. It is expected to increase by 16-20% within 2026. And for underwater welders, the amount can be up to $120000/year.
Mig welders can earn $16.24/hours on average, Rig welders can earn $37/hours, fabricators can earn $17.76/hours and underwater welders can earn up to $26/hour on average.
Which weld process to start with
For beginners I recommend mig welding as it is easy to learn and easy to perform. You just need to learn holding the torch and usage of gas mixture for welding.
Then another welding technique that is beginners friendly is stick welding. Tig welding is a seam less welding technique. If you want perfect welding with perfect finish you should go for tig welding. And for gas less mig welding, you can try flux core welding. All the techniques can weld almost any metals.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Question)
1. What type of welding is the strongest?
So after tig welding when the metal solidifies, a strong bond is created.
2. Do I need a welding certificate from a program or school?
But for professional work and getting welding job, you must have a certificate from a well-known weld school or any short course program.
You need to know the procedures, standards and rules of AWS, and safety precaution when welding in a big project like bridge construction, ship welding, underwater welding, fuel tank welding or in factory.
To do the job you must have academic certificate on welding.
3. Can I teach myself to weld at home?
4. Is welding hard to learn?
As they are dangerous and require high proficiency to do the work.
5. What are the 5 fundamentals of welding?
6. What are the basic principles of welding?
These elements work in harmony on the workpiece, creating a strong, unified bond.
7. What is 5S in welding?
1. Sort: Organize and eliminate unnecessary items.
2. Set in Order: Arrange tools and materials for easy access.
3. Shine: Keep the workplace clean and well-maintained.
4. Standardize: Establish consistent practices for efficiency.
5. Sustain: Maintain the organized and efficient workspace over time.
8. What is PPE for welding?
9. What are 3 safety rules for welding?
Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation to prevent inhalation of welding fumes; work in well-ventilated areas or use exhaust systems.
Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, remove flammable materials from the welding area, and be aware of emergency procedures.
10. What is G in welding?
The letter “G” is part of the American Welding Society (AWS) welding symbol system used to specify the desired weld configuration.
11. What is 2T 4T in welding?
2T (Two-Touch): The welder controls the welding process by pressing and releasing the trigger. It’s a simple on-off control.
4T (Four-Touch): The welder activates the welding process by a short press of the trigger, and it continues without holding it down. Another press stops the welding. It provides a more relaxed operation for longer welds.
Lastly
Welding can be fun at the same time dangerous. So be ready to face the challenge if you want to learn welding. If you follow the rules and tips, welding can be a life changing experience for you. And if fail to do so, it can be a nightmare.
Source:
Check out Our Guide On
