Duty cycle is a measurement of running time of a welder machine. It simply measures how long a welder machine will run continuously without stopping in a selected timeframe.
It is important to consider duty cycle while choosing a welder machine.
In this guide we will delve into duty cycle, how it works and how you can calculate that.
So lets start-
What Is Duty Cycle
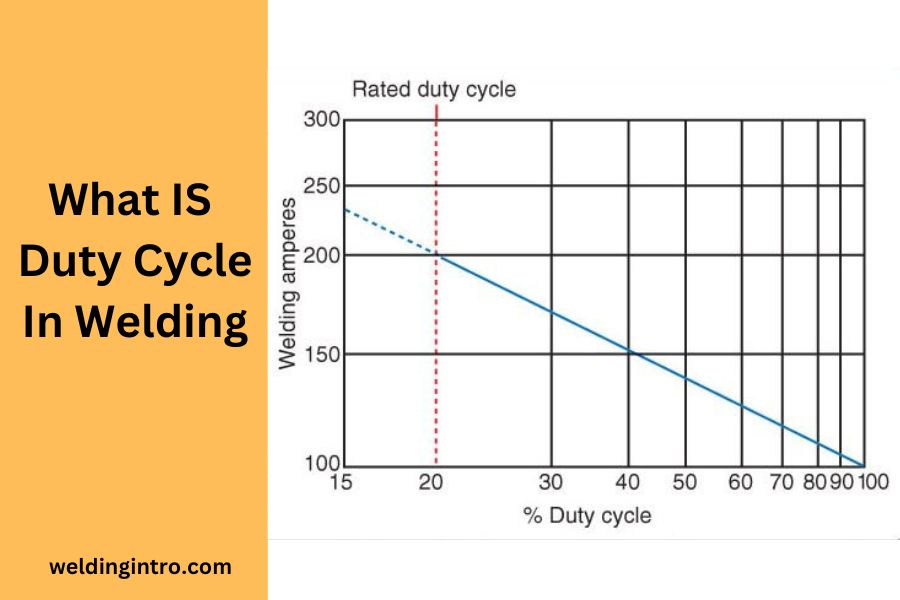
The duty cycle in welding refers to the proportion of time a welding machine can operate within a given time frame without overheating.
It is usually represented as a duty cycle percentage and indicates the ratio of welding time to the total time, considering both the welding and cooling periods.
For example if a welder has a 30% duty cycle in 10-minute time period at 210 amp means the welder will run for 3 minutes continuously at the input power of 210 amperage and after 3 minutes it will automatically shut down for cooling purpose to prevent overheating.
This automatic discontinuation facility is the result of thermal overload protection. It is a technology presented in almost every welding machine. It helps to automatically cut the power supply when the welder machine reaches at specific temperature.
Machines with high duty cycles are generally preferred for continuous or heavy-duty continuous welding applications.
Does Duty Cycle Changes At Different Amperage
Yes, duty cycle fluctuates based on amperage settings in welding equipment. For higher input power or amperage, duty cycle would be lower as increased welding current leads to excessive heat production, requiring longer cooling periods to prevent overheating.
For example if you employ 210 amp power, it would cause the welder temperature to rise more rapidly. The heat would force the overload thermal protection to stop the welder more quickly than usual and take more time to cool down. In most cases, for 210 amp input, duty cycle is 30%.
Meaning it will run continuously for 3 minutes and after that automatically shut down for 7 minutes in a 10 minute time frame for cooling down purpose.
On the other hand, if employed amperage decreases duty cycle increases for inverse causation. For example, for 110 amp input duty cycle can be 100%, meaning it won’t need to stop running to cool down at all.
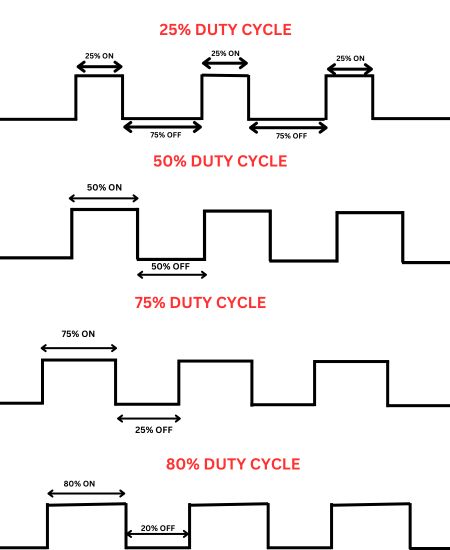
How Can You Calculate Duty Cycle
Basic formula to calculate duty cycle is as follows-
Duty Cycle= (Time of welding/Total time) x100
Here, Time of welding refers to the number of minutes you are actively welding and total time means the time frame. Standard total time is 10 minutes in most of the machines.
Lets use the formula practically to understand more clearly. Suppose you are welding for 3 minutes in a 10 minutes time frame. Just put the numbers into the formula.
The duty cycle for your machine would be-
Duty Cycle= (3/10) x100
=30%
It means your welder would perform a continuous weld for 3 minutes and rest of the 7 minutes it would cooling down. I hope you understand the formula of determining the correct duty cycle.
What Factors Do Affect Duty Cycle
There are few factors that affect the duty cycle. They are
- Ambient Temperatures: The higher the temperature, the lower the duty cycle requiring more time to cool the machine down. And the lower the temperature, the higher the duty cycle.
- Time Period: It is an important factor. It describes the time period over which welding would go on. The Most demanding time period is10 minutes. Few use 5 minutes as a time frame also.
- Machine Condition: Using a welder machine over time reduces its capacity. So is true for the duty cycle.
- Cooling system: Advanced and updated cooling system can increase the duty cycle enabling it to run for extended periods.
- Maintenance: Proper maintenance can increase the lifetime of a welder machine. So a properly maintained machine can hold the same duty cycle it had when it was new.
Testing Duty Cycle
The widely used method for testing duty cycle is the European method. It is a popular one and is called the European standard EN60974-1.
This standard is considered to be the best testing method for evaluating the machine’s performance. Most of the brands use the standard for their products.
There is another testing standard that is made based on European method. And it is Australian standard AS60974-1.
Testing Process
Let’s consider the Lincoln POWER MIG® 211A MIG welder. Its official duty cycle is 30% at 175A, 100% at 90A & 30% at 230V. They have used EN60974-1 standard to test its duty cycle.
- First they run the welder to warm up and continue until the power supply is cut off at least for 2 times.
- Then the machine was sent to a 40◦C heated chamber.
- At last, they run the welder at maximum power (230a) amperage output and weld it for 3 minutes continuously. After 3 minutes the welder restarted. That’s how the welder duty cycle is 30% at 230v power.
Does All Welder Follow The Same Testing Rule
Not all welders follow the same testing formula. I have said that most of the welders use either EN60974-1 or AS60974-1 standard for testing duty cycle. There are many welders that test the welder on their own standard.
So we cannot compare two welders duty cycle if they follow different welding standards.
Also we know that there are multiple factors that affect duty cycle. For example, welding machine condition, time frame and temperature. So if two machines do not follow similar mentioned factors, then there can be no comparison.
Duty Cycle In Different Process
Duty cycle differs based on the welding processes. Few processes require a higher duty cycle and few demands lower.
1. Mig & Duty cycle
Mig wedding is a semi-automatic process. Here the wire feeder continuously feeds wire into the weldment. So a mig welder needs to run for a long period of time with minimum down time.
Of course it depends on the application. So the more duty cycle, the better for mig welding.
2. Tig and duty cycle
Tig welding is used for detailed work. In thinner metal and for precision tig welding is best. So most of the time it doesn’t reach the overload thermal point. Welders in tig welding require time to aesthetically weld the material.
So welders don’t need to run continuously which reduces the importance of higher duty cycles. In tig welding duty cycle doesn’t matter the most.
3. Mma/stick welding and duty cycle
Stick welding is a manual technique where welders need to change electrodes, ground clamp and position. Compared to mig welding less welding is actually done in stick welding. So, the duty cycle is not that crucial in stick welding.
Even 30% duty cycles sometimes tend to be high in the MMA process.
The Importance Of Duty Cycle In Welding
Duty cycle is important when choosing a welder. It expresses productivity and performance of a welder machine.
How much time a machine would take to weld a specific metal, can be determined from the duty cycle rating. The higher the duty cycle, the more powerful the machine is.
Also, duty cycle describes the durability of the machine as it protects the IGBT transistor, rectifiers and transformers. If there is no overload thermal protection, then the machine would overheat and cause an accident.
So it is important to consider the duty cycle of a welder machine.
What Happens When The Duty Cycle Is Exceeded
When the output power exceeds the duty cycle, the machine automatically shuts off. It is due to the overload thermal protection that helps to cut the power supply from the transformer when the machine is overheated.
Machine doesn’t turn on until it fully cools down. Thus the machine is prevented from being melted down inside.
The Advantages of Duty Cycle in Welding
- Prevents accidents: As we know, duty cycles prevent the machine from being burnt inside. So while the machine is overheated it would automatically turn off. As a result no fire accidents would happen
- Retain Focus: If you weld for an extended time chances are you would make mistakes. So the duty cycle helps here as it restarts after a specific time. Which lets you focus on the work.
Disadvantages of Duty Cycle
- Constant interruption: It is sometimes boring and infuriating when you are welding minutely and suddenly it turns off. Sometimes it ruins the welding mode.
- Reduce quality: Sometimes machines turn off at a peak moment. When you are giving the finishing touch and at the time the machine turns off due to the duty cycle, it can ruin the quality of the weld.
What is a good duty cycle?
It depends on many factors. Most importantly on the welding process. Mig welding requires higher duty cycle and above 50% is appreciated in Mig. While the stick welding and tig welding, the duty cycle need not to be that higher.
Duty cycle below 50% would do the work in these case. Even as low as 20% duty cycle would make no difference in Tig and MMA process.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a 100% duty cycle?
100% duty cycle means a welding machine can run continuously without overheating or needing a break. This type of welders are ideal for applications where non-stop welding is required.
2. What is the formula for duty cycle?
Duty Cycle= (Total cycle time/Welding time)×100
3. What does duty cycle based mean?
Duty cycle based Refers to a specification or decision determined by the duty cycle of a device, indicating its ability to operate continuously without overheating.
4. What is a 50% duty cycle?
A welding machine of 50% duty cycle can operate for half the total cycle time, making it suitable for intermittent welding tasks with breaks to prevent overheating.
5. Why is duty cycle important?
Duty Cycle indicates a welding machine’s ability to handle continuous operation without overheating, helping users choose equipment suitable for their work requirements and preventing damage due to prolonged use. For that reason duty cycle is important.
6. How is duty cycle controlled?
Duty Cycle is managed by incorporating cooling systems, efficient design, and thermal protection mechanisms in welding machines. It maintains optimal temperature during operation, preventing overheating.
7. Can duty cycle be over 100?
No, Duty Cycle Cannot Exceed 100%. Exceeding 100% implies continuous operation beyond the specified limits, risking overheating and potential damage which is not possible.
Lastly
If a welder doesn’t know about the features of his machine then he/she can not be an expert in the field. A good welder machine is the first priority for a professional and a newbie welder.
And the duty cycle is one of the important features that the machines provide. So every welder must have knowledge of the duty cycle.
Also check
Our Guide On: Weld terminology
